In the intricate symphony of human movement, muscles play the lead role, orchestrating every step, lift, and leap. Yet, like any virtuoso, they too require moments of respite and rejuvenation to maintain their harmonious performance. Enter stretching—a timeless practice, often overlooked, yet pivotal in the recovery narrative of our muscular ensemble. As we delve into the role of stretching in muscle recovery, we explore how this simple, yet profound, act serves not only as a prelude to activity but as a vital postlude that aids in healing and renewal. Through the lens of science and the art of movement, we unravel how stretching can transform recovery from a mere pause into a powerful tool for muscular resilience and longevity.
Understanding the Science Behind Stretching and Muscle Recovery
Stretching is often hailed as a cornerstone of effective muscle recovery, offering a myriad of benefits that extend beyond simple flexibility. When you stretch, you engage in a process that enhances blood circulation, delivering oxygen and essential nutrients to tired muscles. This increased blood flow can expedite the removal of metabolic waste products, such as lactic acid, which often accumulate during intense physical activity. Furthermore, stretching aids in maintaining the elasticity of muscle fibers, reducing the likelihood of injuries.
- Improved Flexibility: Regular stretching helps in maintaining and improving flexibility, which is crucial for optimal muscle function.
- Enhanced Blood Flow: By promoting circulation, stretching supports the transport of nutrients and oxygen, accelerating recovery.
- Injury Prevention: Maintaining muscle elasticity through stretching reduces the risk of strains and sprains.
- Reduced Muscle Tension: Stretching can alleviate muscle tightness, reducing discomfort and enhancing overall relaxation.
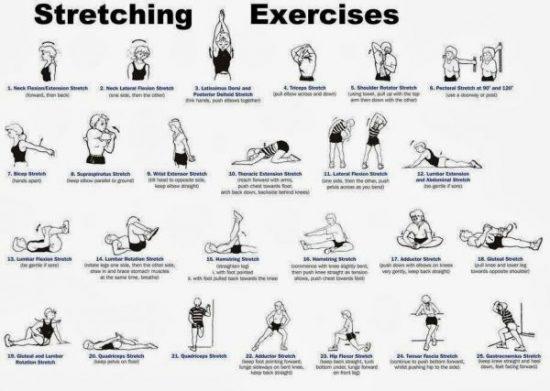
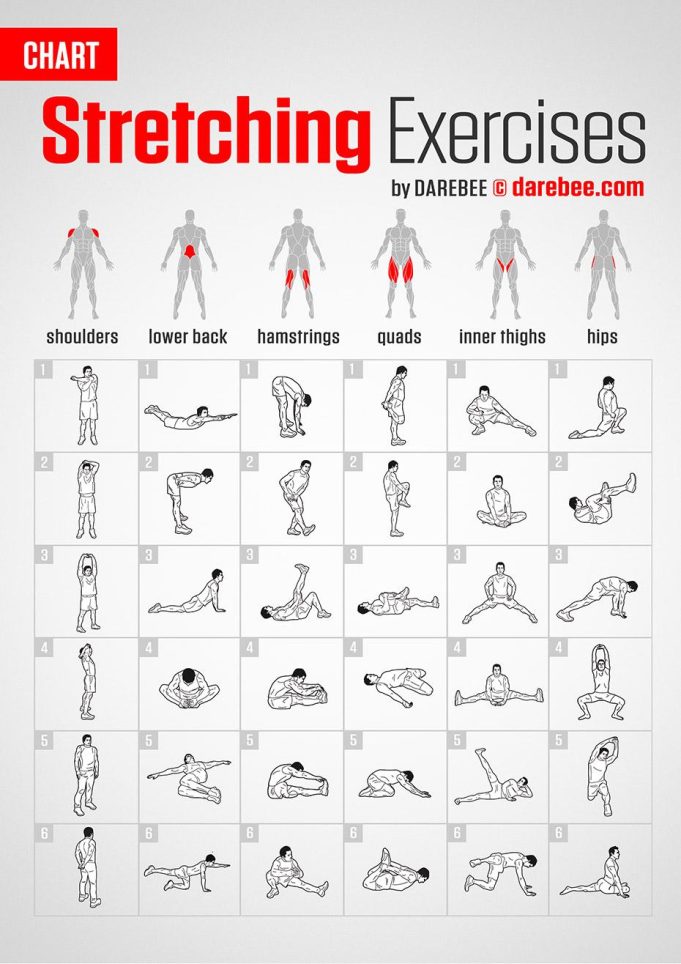
How Stretching Techniques Influence Healing and Performance
Incorporating various stretching techniques into your routine can significantly impact both the healing process and athletic performance. Stretching enhances blood flow to the muscles, which is crucial for delivering nutrients and oxygen that aid in tissue repair. Dynamic stretching, which involves active movements that stretch the muscles to their full range of motion, is particularly effective when performed before workouts. This technique helps increase muscle temperature and elasticity, preparing the body for intense physical activity while reducing the risk of injury.
On the other hand, static stretching is best utilized after workouts. By holding stretches for extended periods, typically 15 to 60 seconds, this method aids in the removal of lactic acid buildup, reducing muscle stiffness and soreness. PNF (Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation) stretching, a combination of passive stretching and isometric contractions, can further enhance flexibility and muscle recovery. Consider incorporating the following stretching techniques into your routine:
- Dynamic Stretching: Ideal for warm-ups, involving movements like leg swings and arm circles.
- Static Stretching: Best for cooldowns, focusing on stretches like hamstring and quadriceps holds.
- PNF Stretching: Advanced technique, often requiring a partner, to deepen flexibility.
By understanding and applying these techniques, you can create a balanced stretching regimen that not only accelerates recovery but also enhances overall performance.

Incorporating Stretching into Your Post-Workout Routine
Adding stretching to your post-workout routine can significantly enhance muscle recovery, promoting flexibility and reducing the risk of injury. When muscles are warm after exercise, they are more pliable, making it an ideal time to incorporate a few stretches. This can help in lengthening the muscle fibers and improving overall mobility. Stretching not only aids in relieving muscle tension but also helps in dispersing lactic acid build-up, which can reduce soreness. To make the most of your stretching routine, focus on major muscle groups that were engaged during your workout.
- Improved Flexibility: Regular stretching increases your range of motion.
- Enhanced Circulation: Stretching boosts blood flow to the muscles, aiding in recovery.
- Stress Relief: A calming stretch can help in reducing post-exercise stress and tension.
- Prevention of Injuries: By maintaining flexibility, stretching reduces the risk of muscle strains.

Expert Tips for Effective Stretching to Enhance Recovery
Unlock the full potential of your recovery routine with these expert-approved stretching techniques. Emphasizing proper form and consistency can lead to significant improvements in muscle recovery. Consider the following tips:
- Focus on Form: Ensure that your body is properly aligned during each stretch to maximize effectiveness and minimize the risk of injury. Pay attention to your breathing, as deep breaths can enhance relaxation and increase the stretch’s benefits.
- Dynamic vs. Static: Incorporate both dynamic and static stretching into your routine. Dynamic stretching, which involves movement-based stretches, is ideal before workouts to prepare muscles. Static stretching, where stretches are held for a period, is more beneficial post-exercise to aid recovery.
- Consistency is Key: Make stretching a regular part of your routine, not just an afterthought. Consistent stretching can improve flexibility, reduce muscle stiffness, and enhance overall recovery.
By integrating these techniques into your regimen, you’ll not only speed up recovery but also improve your overall physical performance. Remember, stretching is not just a recovery tool; it’s an essential component of a balanced fitness routine.